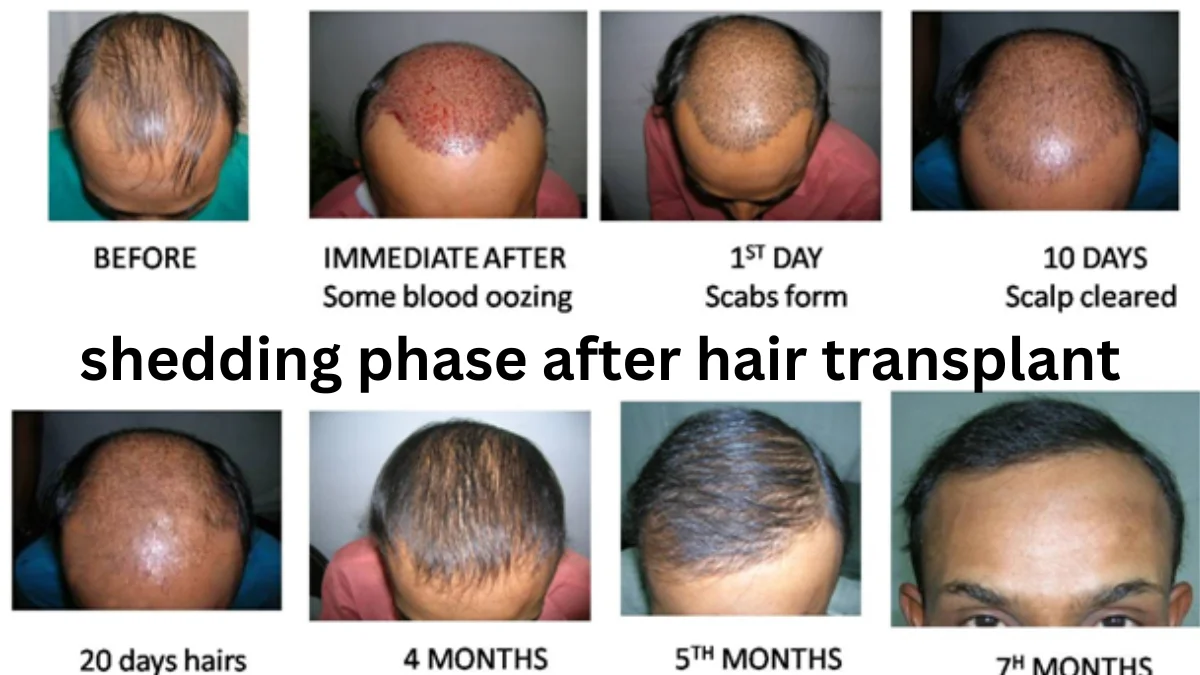
Undergoing a hair transplant is an exciting step toward hair restoration, but many individuals experience the shedding phase shortly after the procedure. This stage, also known as shock loss, is a natural and temporary process. Understanding the shedding phase can help manage expectations and ensure proper scalp care for optimal regrowth.
Book Your Consultation Today
Visit Dr. Hanan Dermatology Specialty Clinic in Padur, OMR, Chennai. Schedule your consultation today and start your journey to fuller, healthier hair.
For more information and to book your appointment, visit our clinic or call us at the clinic’s contact details.
What is the Shedding Phase?
The shedding phase is a temporary period where transplanted hair falls out before new growth begins. This happens because the hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle after being relocated. While shedding may seem concerning, it is a normal and necessary part of the hair restoration journey.
When Does Shedding Occur?
- Shedding typically begins 2–4 weeks after a hair transplant.
- The phase can last for 2–3 months, depending on individual healing factors.
- You may first notice a few hairs falling out, which gradually becomes more noticeable.
Why Does Shedding Happen?
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): Active hair growth stage.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): Hair stops growing and prepares to shed.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): Hair falls out before new hair grows.
After a transplant, hair follicles enter the telogen phase due to temporary trauma, leading to shedding. However, the follicles remain intact and will soon produce new hair.
What Happens After Shedding?
- 4–12 Months: New hair begins to grow back.
- 12–18 Months: Hair becomes thicker and blends with existing hair.
- The final results depend on individual hair growth rates and adherence to post-transplant care.
How to Care for the Scalp During Shedding

Proper scalp care can promote healing and support new hair growth. Follow these essential tips:
- Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo to avoid irritation.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing the scalp.
- Pat dry with a soft towel instead of rubbing.
- Keep the scalp hydrated with doctor-recommended products.
- Protect from sun exposure by wearing a hat or using scalp-friendly sunscreen.
Read more: Things to Do Before Getting a Hair Transplant
Can Shedding Be Reduced?
While shedding is unavoidable, certain treatments can help minimize it:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections can boost hair follicle recovery and reduce excessive shedding.
- Medications: Doctors may recommend Minoxidil or Finasteride to support new hair growth and reduce post-transplant shedding.
Common Myths & Misconceptions
Myth 1: Shedding Means the Transplant Failed
Fact: Shedding is a normal part of the hair transplant process, and new hair will grow back stronger.
Myth 2: Shedding is Permanent
Fact: The transplanted hair follicles remain intact, and shedding only affects the hair strands, not the roots.
FAQs
1. Is shedding normal after a hair transplant?
Yes, shedding is a normal part of the healing process. It’s known as shock loss and occurs because the transplanted hair follicles enter the resting phase before new hair growth begins.
2. When does shedding start after a hair transplant?
Shedding typically begins 2–4 weeks after the transplant procedure.
3. How long does the shedding phase last?
The shedding phase can last between 2–3 months, depending on individual healing and hair growth cycles.
4. Does shedding mean my hair transplant has failed?
No, shedding does not mean failure. The hair follicles remain intact, and new hair will begin to grow after the shedding phase.
5. When will new hair start growing after shedding?
New hair usually starts to grow within 4–12 months, with significant thickening by 12–18 months.
6. How can I care for my scalp during the shedding phase?
- Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing the scalp.
- Keep the scalp moisturized and protected from the sun.
- Follow doctor-recommended post-care instructions.
7. Can I reduce the shedding phase?
Some treatments can help minimize shedding, such as:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Medications like Minoxidil or Finasteride
8. Will all the transplanted hair shed?
Not all transplanted hair will shed, but it is common for a significant amount to fall out before new growth begins.
9. Can I speed up hair regrowth after shedding?
While there’s no way to completely speed up the process, proper scalp care, a healthy diet, and doctor-recommended treatments can support faster regrowth.
10. What if shedding continues beyond three months?
If shedding persists beyond the expected timeline, consult your hair transplant specialist to rule out any underlying issues.



