Table of Contents
Skin Pigmentation: Types, Symptoms, and Causes
Skin pigmentation refers to the color of the skin, primarily determined by melanin production. While variations are normal, some changes may signal health issues. This guide explores the types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatments of skin pigmentation disorders.
Types of Skin Pigmentation
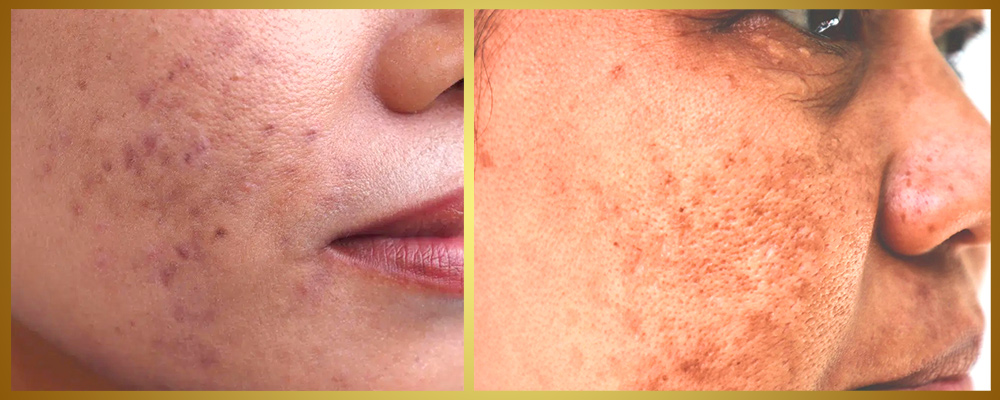
1. Hyperpigmentation
This occurs when certain skin areas darken due to excess melanin. Common types include:
a. Sunspots: Brown spots from sun exposure.
b. Age Spots: Flat brown spots related to aging.
c. Melasma: Dark patches often seen in pregnant women.
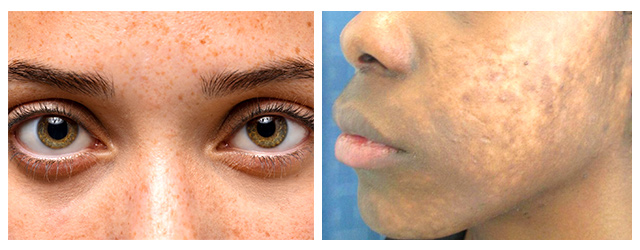
2. Hypopigmentation
This is characterized by lighter patches due to reduced melanin. Notable types include:
a. Vitiligo: An autoimmune disorder causing white patches.
b. Albinism: A genetic condition with minimal melanin.
c. Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Lighter skin after injury or inflammation.
Symptoms of Skin Pigmentation
Symptoms can vary but often include:
a. Discoloration or patches of lighter/darker skin.
b. Uneven skin tone.
c. Sensitivity or irritation in affected areas.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation
The main reasons are:
1. Sunlight: UV rays stimulate the production of melanin, which causes hyperpigmentation.
2. Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in pregnancy or hormone therapy can cause melasma.
3. Genetics: Conditions such as vitiligo and albinism have a genetic component.
4. Inflammation or injury: Injury can cause pigmentation changes while the skin is healing.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a dermatologist if you experience:
1. Sudden changes in pigmentation.
2. Persistent spots that do not improve.
3. A family history of skin conditions.
Diagnosis of Skin Pigmentation
Diagnosis typically involves:
a. Medical History: Understanding triggers and family history.
b. Physical Examination: Assessing affected areas.
c. Biopsy: To rule out skin cancer if necessary.
Treatments for Skin Pigmentation
1. Topical treatment Hydroquinone: Helps fade dark spots. Retinoid: Promotes skin cell turnover.
2. Chemical peeling: These remove the outer layer of skin to improve pigmentation.
3. Laser treatment: Laser treatment targets specific areas. By removing excess melanin.
4. Lifestyle research: Sun protection: Use sunscreen to prevent further pigmentation changes.