Table of Contents
Male Baldness: Types, Symptoms, and Causes
Male pattern baldness or male pattern baldness affects many men. This often results in hair thinning or falling out over time. Understanding the type, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to see a doctor is key to managing it. Below is a brief guide to this condition.
Types of Male Baldness
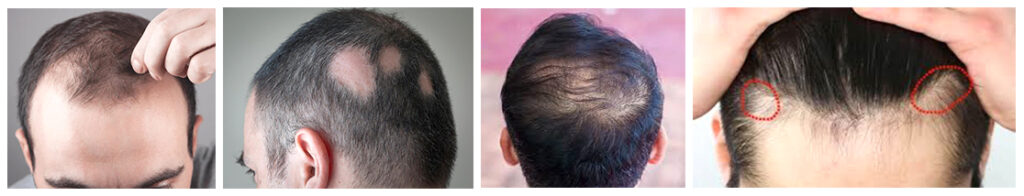
1. Androgenetic Alopecia
Commonly known as male pattern baldness, this follows a receding hairline and thinning at the crown.
2. Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune condition causing sudden bald patches on the scalp.
3. Telogen Effluvium
Temporary hair loss due to stress, illness, or other factors causing hair to enter a resting phase.
4. Traction Alopecia
Hair loss from constant tension or tight hairstyles can become permanent over time.
Symptoms of Male Baldness
a. Receding hairline
b. Thinning at the crown
c. Patchy bald spots
d. Excessive shedding when brushing or washing hair
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you experience:
1. Sudden or rapid hair loss
2. Scalp pain or inflammation
3. Hair loss after stress or illness
4. Worsening bald patches
Causes of Male Baldness
1. Genetics
Testosterone-induced alopecia is the most common cause of inherited alopecia.
2. Hormonal changes
Increased sensitivity to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can cause hair follicles to shrink and lead to baldness.
3. Medical conditions
Autoimmune disease Thyroid disorder And scalp infections can also cause hair loss.
4. Medicine
The same is true for high blood pressure or cancer treatment. Some medicines can cause hair loss.
5. Stress and malnutrition
Stress and lack of essential vitamins such as vitamin D and iron. It may cause your hair to thin as well.
Diagnosis of Male Baldness
a. Scalp examination by a dermatologist
b. Blood tests to check for underlying medical issues
c. Scalp biopsy if infections or skin conditions are suspected
Treatments for Male Baldness
1. Medicine
a. Minoxidil (Rogaine): a topical solution that stimulates hair growth.
b. Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication that reduces DHT levels.
2. Hair transplant
Surgical options such as FUE or FUT move the hair follicles to a thinner area.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Non-invasive laser treatment stimulates hair follicles to grow new hair.
4. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy (PRP)
Platelet injections stimulate hair growth.
5. Lifestyle changes
Improving diet stress management And proper scalp care can slow down hair loss.