OUR PATIENT'S RESULTS
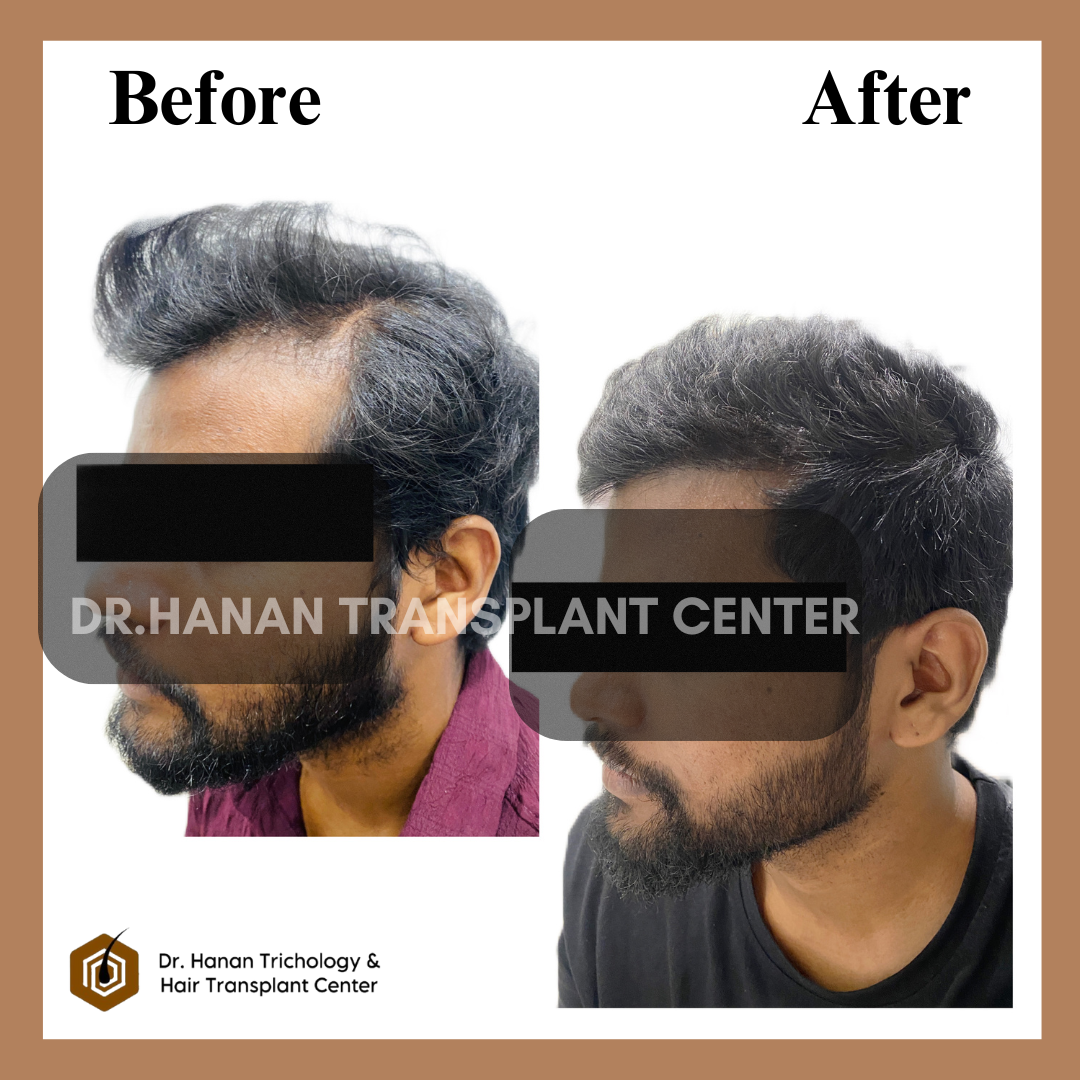

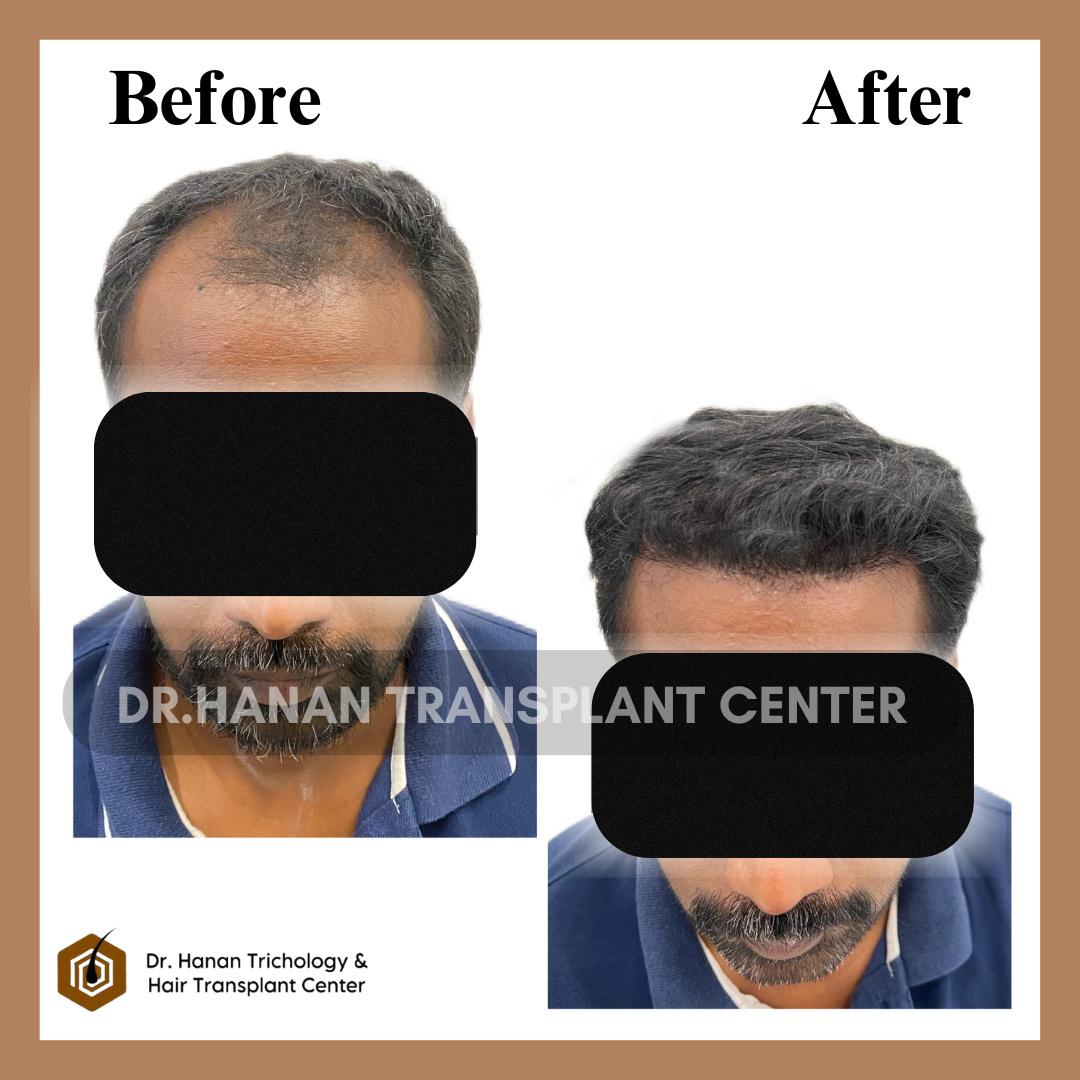
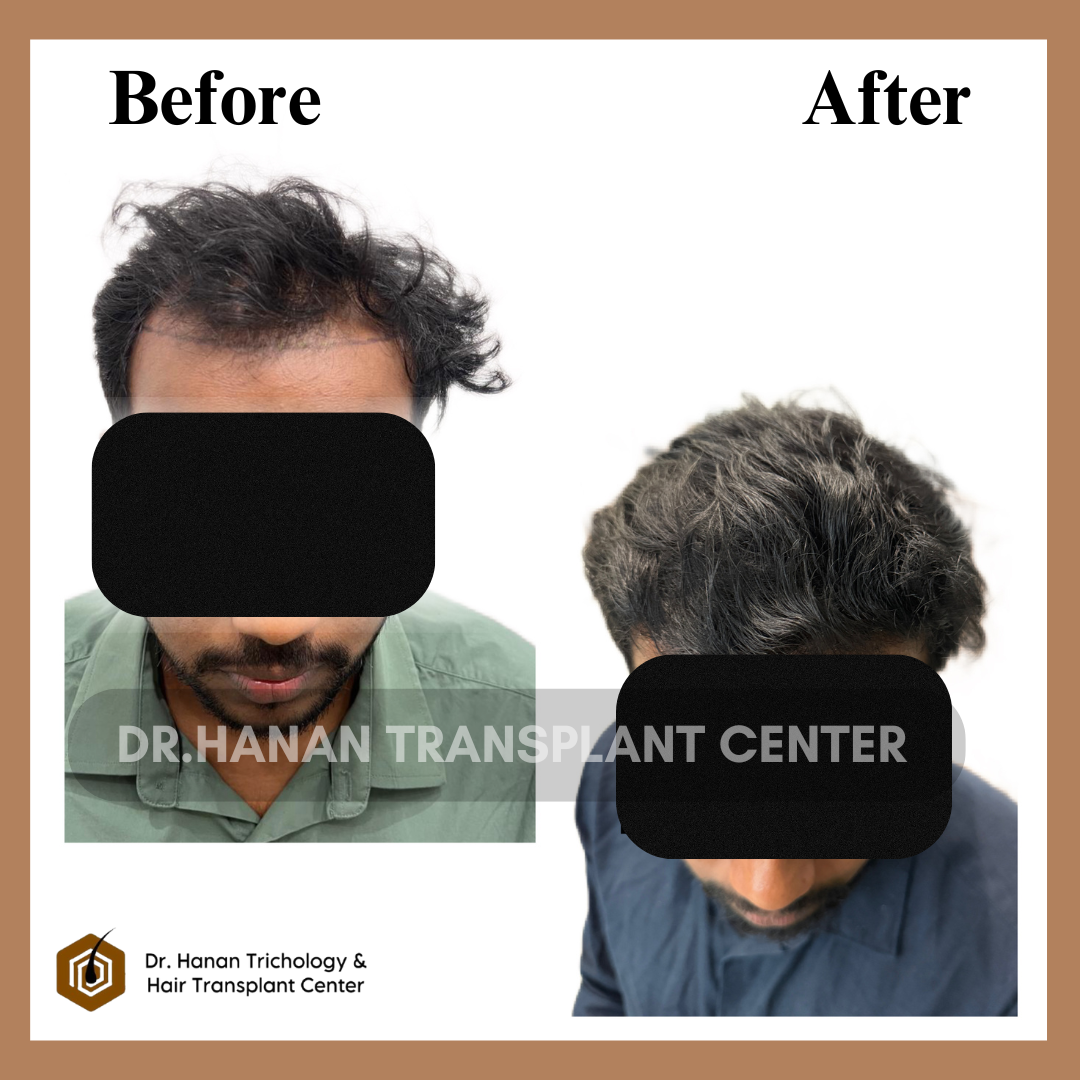
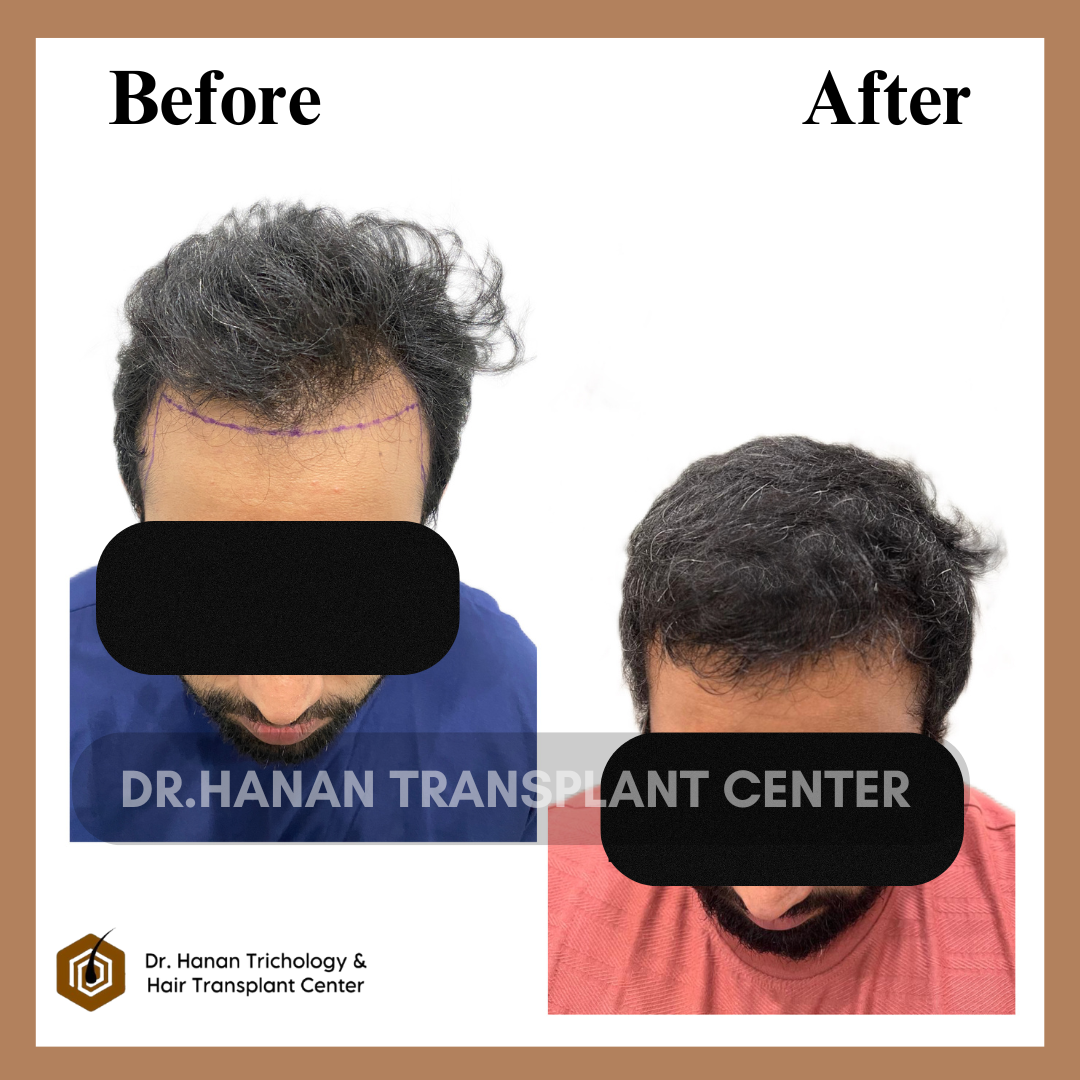
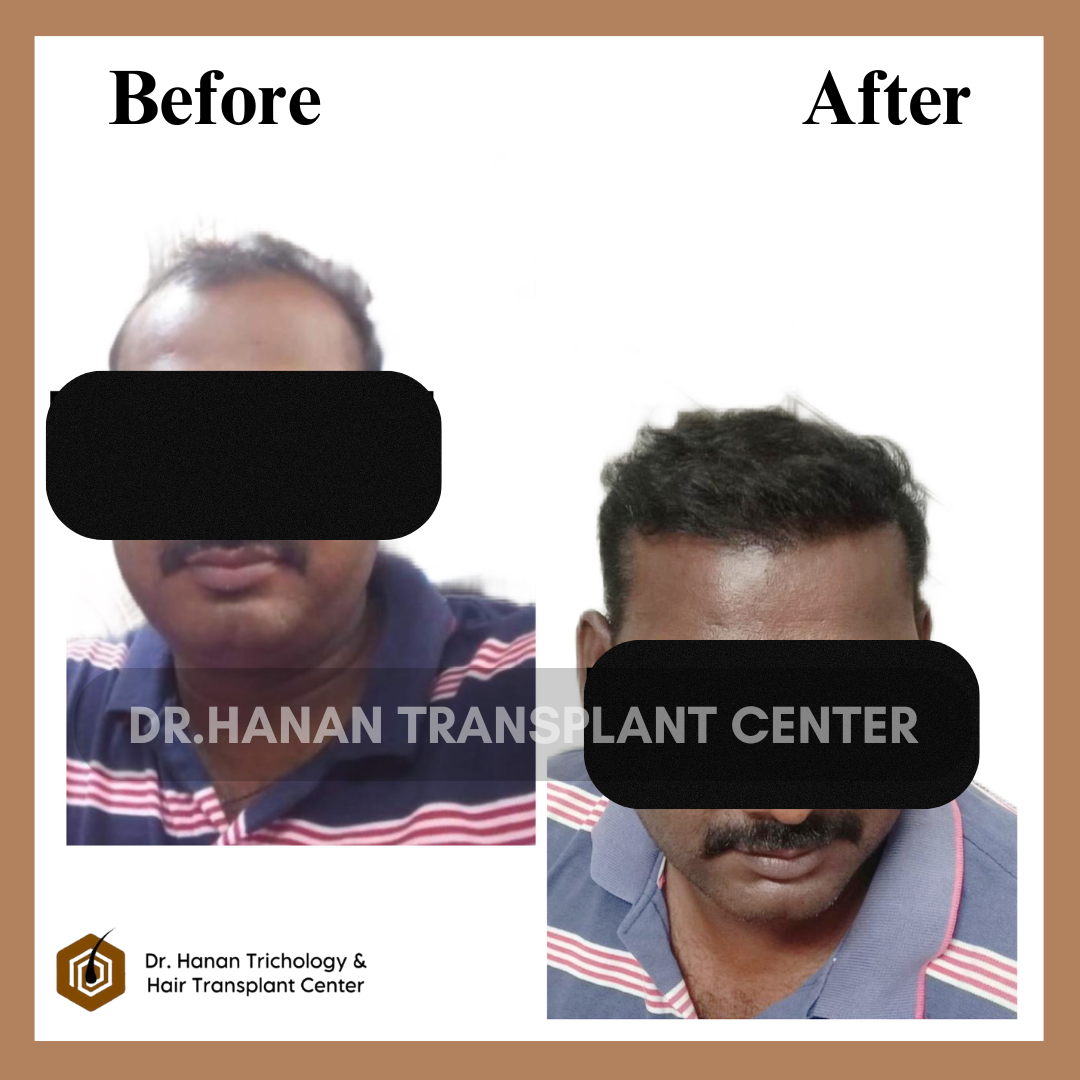
Table of Contents
Hair Transplant: Types, Symptoms, and Causes
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that relocates hair to areas of the scalp that are bald or thinning.
Also known as hair restoration or hair replacement, this option is typically considered by individuals who have already explored other treatments for hair loss.
The procedure is performed by dermatologists, who specialize in skin care, or plastic surgeons, who focus on reconstructive techniques.
Types of Hair Transplants
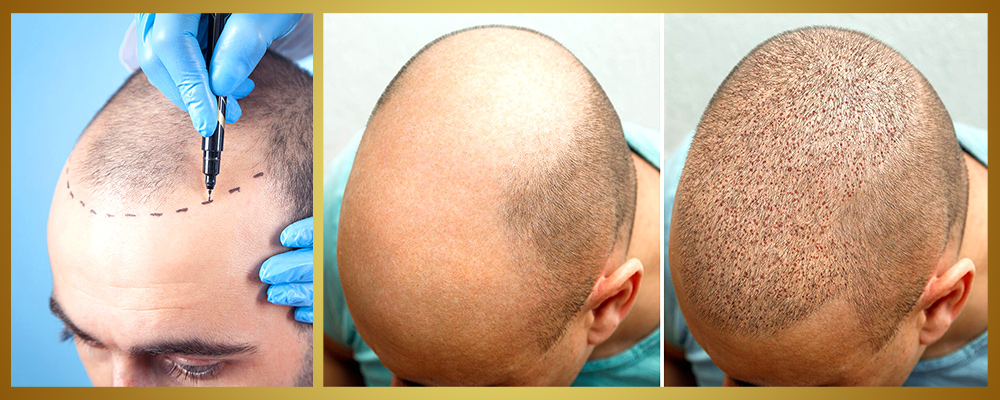
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
This method involves removing a strip of skin from the back of the scalp, from which hair follicles are extracted and then transplanted into thinning or balding areas. FUT is effective for larger areas of hair loss.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the scalp using a specialized tool. This technique minimizes scarring and allows for quicker recovery, making it a popular choice for patients seeking a less invasive option.
3. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
DHI combines extraction and implantation in one step, using a pen-like instrument to implant hair follicles directly into the recipient area without incisions. This method allows for precise placement and reduces scalp trauma.
Symptoms of Hair Loss
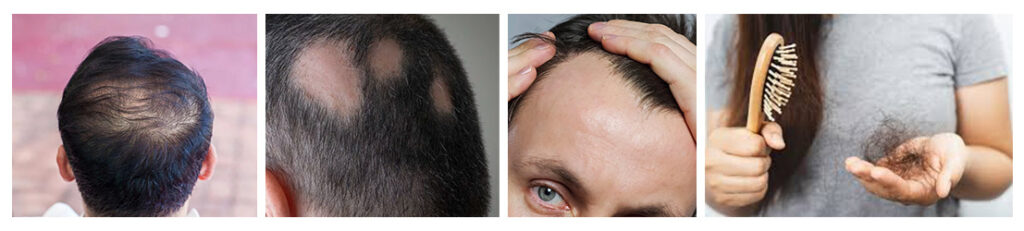
a. Thinning hair: The density of the hair decreases gradually. It is often observed while styling or washing your hair.
b. Bald spots: Hair falls out in patches. It is often associated with symptoms such as patchy hair loss.
c. Receding hairline: Significant hair loss at the temples or forehead. Commonly found on the bald spots of men.
d. Excessive shedding: Losing more than 100 strands of hair per day, which may indicate a medical problem or stress.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if you experience:
1. Sudden or unexplained hair loss.
2. Persistent scalp issues like itching, redness, or flaking.
3. Hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue or weight changes.
4. A family history of severe hair loss or baldness at a young age.
Causes of hair loss
a. Genetics: Genetic factors play an important role in conditions such as pattern baldness in both men and women.
b. Hormonal changes: Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause. May cause hair loss.
c. Medical conditions: Diseases such as thyroid disorders autoimmune disease and scalp infections It may cause hair to thin or fall out.
d. Stress and trauma: Emotional or physical stress can cause temporary hair loss called telogen effluvium.
e. Malnutrition: Lack of essential nutrients such as iron, protein, and vitamins can cause hair to thin.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hair loss typically involves:
1. Medical History Review: Discuss your medical history and family background with your doctor.
2. Physical Examination: Examining the scalp to determine the pattern and extent of hair loss.
3. Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check for hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies, and scalp biopsies if needed.
Treatments
1. Medications:
a. Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that promotes hair growth.
b. Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication that slows hair loss in men.
2. Hair Transplant Surgery:
a. FUT or FUE procedures to relocate hair follicles from donor areas to thinning spots.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy:
A non-invasive treatment that uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
Involves injecting PRP derived from your blood into the scalp to promote hair growth.